Case Reports
29 May 2023
Vol. 17 No. 1 (2023)
Adult-onset Still’s disease with secondary macrophage activation syndrome: a case report
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1424
Views
458
Downloads
53
HTML
Authors
Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera, Italy.
Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera, Italy.
Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera, Italy.
Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera, Italy.
Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera, Italy.
Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera, Italy.
Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera, Italy.
Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera, Italy.
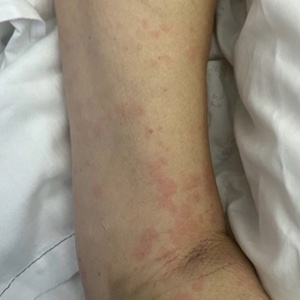
We describe a case of adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) with secondary macrophage activation syndrome. AOSD is a rare disease with unknown origin. Rarely it’s complicated by secondary macrophage activation syndrome, which is a life-threatening disorder. Because the diagnosis of AOSD is essential for exclusion and complications are life-threatening, it is mandatory for a prompt and extensive diagnostic workup and treatment.
Magadur-Joly G, Billaud E, Barrier JH, et al. Epidemiology of adult Still’s disease: estimate of the incidence by a retrospective study in west France. Ann Rheum Dis 1995;54:587-90. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.54.7.587
Castaneda S, Blanco R, Gonzalez-Gay MA. Adult-onset Still’s disease: advances in treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2016;30:222-38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2016.08.003
Efthimiou P, Kontzias A, Hur P, et al. Adult-onset Still’s disease in focus: clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and unmet needs in the era of targeted therapies. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2021;51:858-74. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.06.004
Yamaguchi M, Ohta A, Tsunematsu T, et al. Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still’s disease. J Rheumatol 1992;19:424-30.
Al-Samkari H, Berliner N. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Annu Rev Pathol Mech Dis 2018;13:27-49. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-020117-043625
Crayne CB, Albeituni S, Nichols KE, et al. The immunology of macrophage activation syndrome. Front Immunol 2019:10:119. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00119
Jordan MB, Hildeman D, Kappler J and Marrack P. An animal model of hemophagocitic lymphoistiocytosis (HLH); CD8 T cells and interferon gamma are essential for the disorder. Blood 2004;104:735-43. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2003-10-3413
Schulert GS, Cron RQ. The genetics of macrophage activation syndrome. Genes Immun 2020;21:169-81. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41435-020-0098-4
Kaufman KM, Linghu B, Szustakowski JD, et al. Wholeexome sequencing reveals overlap between macrophage activation syndrome in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014;66:3486-95. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38793
Dhore R, Simon J, Papo T, et al. Reactive hemophagocitic syndrome adult systemic disease: report of twenty-six cases and literature review. Arthritis Rheum 2003;49:633-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/art.11368
Fukaya S, Yasuda S, Hashimoto T, et al. Clinical features of hemophagocytic syndrome in patients with systemic autoimmune disease: analysis of 30 cases. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47:1686-91. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ken342
Yang XP, Wang M., Li TF, et al. Predictive factors and prognosis of macrophage activation syndrome associated with adult-onset Still’s disease. Clin Expe Rheumatol 2019:37:83-8.
Fardet L, Galicier L, Lambotte O, et al. Development and validation of the HScore, a score for the diagnosis of reactive
hemophagocytic syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014;66:2613-20. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38690
Henter JI, Horne A, Arico’ M, et al. HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2007;48:124-31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.21039
Fajgenbaum D, June C. Cytokine Storm. NEJM 2020; 383:2255-73. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra2026131
Giuseppe Nicoletti, Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera
Internal Medicine director
Antonio Bonelli, Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera
MD
Rocco Clemente, Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera
MD
Simona Ciuffreda, Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera
MD
Gaetano Dentamaro, Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera
MD
Agata Tiziana La Masa, Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera
MD
Vito Lascaro, Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera
MD
Pasquale Santarcangelo, Internal Medicine, Madonna delle Grazie Hospital, Matera
MD
How to Cite
Copyright (c) 2023 the Author(s)


This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.






